JDBC Statement trong java (Bài 4)
Thông qua bài JDBC Statement trong java chúng tôi sẽ hướng dẫn các bạn cách thực thi các câu lệnh sql từ java. Cụ thể, khi một kết nối được thiết lập, chúng ta có thể tương tác với cơ sở dữ liệu.
JDBC Statement, PreparedStatement và CallableStatement định nghĩa những phương thức và thuộc tính, cho phép chúng ta thực thi câu lệnh SQL và nhận dữ liệu từ cơ sở dữ liệu của bạn.
Bảng sau đây mô tả tóm tắt về Statement, PreparedStatement và CallableStatement
| JDBC Statements | Mục đích sử dụng |
|---|---|
| Statement | Hữu ích khi bạn đang sử dụng câu lệnh SQL tĩnh khi chạy. Statement không chấp nhận tham số (parameters). |
| PreparedStatement | PreparedStatement cho phép chỉ định tham số đầu vào khi chạy. |
| CallableStatement | Sử dụng khi bạn muốn truy cập stored procedures. CallableStatement cũng chấp nhận tham số đầu vào khi chạy. |
JDBC Statement trong java – Đối tượng Statement (Statement Objects)
Tạo đối tượng Statement
Statement stmt = null;
try {
stmt = conn.createStatement( );
. . .
}
catch (SQLException e) {
. . .
}
finally {
. . .
}
Thực thi câu lệnh SQL (Execute an SQL statement)
- boolean execute (String SQL): Trả về giá trị true nếu thực thi thành công câu lệnh SQL; ngược lại sẽ trả về giá trị false. Sử dụng phương thức này để thực thi các câu lệnh SQL DDL như tạo cơ sở dữ liệu, tạo bảng, …
- int executeUpdate (String SQL): Trả về số dòng bị tác động khi thực thi các câu lệnh như INSERT, UPDATE hoặc DELETE.
- ResultSet executeQuery (String SQL): Trả về một đối tượng ResultSet khi bạn thực thi câu lệnh SELECT.
Đóng đối tượng Statement (Closing Statement Object)
Statement stmt = null;
try {
stmt = conn.createStatement( );
. . .
}
catch (SQLException e) {
. . .
}
finally {
stmt.close();
}
JDBC Statement trong java – Ví dụ chương trình Java kết nối đến máy chủ localhost, thực hiện truy cập vào cơ sở dữ liệu tên EMPDB sử dụng tài khoản sa, mật khẩu sa. Ứng dụng thực hiện thêm mới (thực thi câu lệnh insert) một nhân viên vào bảng Employee và thực hiện xem dữ liệu (thực thi câu lệnh select) của bảng này.
package jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
*
* @author giasutinhoc.vn
*/
public class JDBCStatementExample {
// SQL Server JDBC connection string
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:sqlserver://localhost;databaseName=EMPDB;user=sa;password=sa";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
//Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL);
//Execute a query
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "INSERT INTO Employees VALUES (100, 18, N'gia sư', N'tin học');";
int rows = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("Rows impacted : " + rows);
// Let us select all the records and display them.
sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Employees";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//Extract data from result set
while (rs.next()) {
//Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last");
//Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
}
//Clean-up environment
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
//Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
} catch (SQLException se2) {
}// nothing we can do
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
}//end finally try
}//end try
System.out.println("Done!");
}
}
JDBC Statement trong java – Đối tượng PreparedStatement (PreparedStatement Objects)
Tạo đối tượng PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
String SQL = "Update Employees SET age = ? WHERE id = ?";
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(SQL);
. . .
}
catch (SQLException e) {
. . .
}
finally {
. . .
}
Tất cả các tham số được đại diện bởi ?, bạn phải cung cấp giá trị cho tất cả các tham số số trước khi thực hiện các câu lệnh SQL bằng cách sử dụng phương thức setXXX() với XXX đại diện cho kiểu dữ liệu. Và mỗi tham số được đánh dấu bằng số thứ tự; tha số đầu tiên có vị trí là 1, tham số kế tiếp có vị trí là 2, …
Đóng đối tượng PreparedStatement
pstmt.close();
Ví dụ
package jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
*
* @author giasutinhoc.vn
*/
public class JDBCPreparedStatementExample {
// SQL Server JDBC connection string
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:sqlserver://localhost;databaseName=EMPDB;user=sa;password=sa";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
try {
//Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL);
//Execute a query
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
String sql = "UPDATE Employees set age=? WHERE id=?";
stmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//Bind values into the parameters.
stmt.setInt(1, 35); // This would set age
stmt.setInt(2, 100); // This would set ID
// Let us update age of the record with ID = 100;
int rows = stmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("Rows impacted : " + rows);
// Let us select all the records and display them.
sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Employees";
stmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery();
//Extract data from result set
while (rs.next()) {
//Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last");
//Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
}
//Clean-up environment
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
//Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
} catch (SQLException se2) {
se2.printStackTrace();
}// nothing we can do
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
}//end finally try
}//end try
System.out.println("Done!");
}
}
JDBC Statement trong java – Đối tượng CallableStatement (CallableStatement Objects)
Tạo đối tượng CallableStatement (Creating CallableStatement Object)
CallableStatement cstmt = null;
try {
String SQL = "{call ProcedureName (?, ?)}";
cstmt = conn.prepareCall (SQL);
. . .
}
catch (SQLException e) {
. . .
}
finally {
. . .
}
Đóng đối tượng CallableStatement (Closing CallableStatement Object)
cstmt.close();
Ví dụ
Tạo thủ tục getEmpName trong EMPDB sử dụng Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio
GO USE EMPDB GO CREATE PROCEDURE getEmpName @EMP_ID INT, @EMP_FIRST NVARCHAR(255) OUTPUT AS BEGIN SELECT @EMP_FIRST = first FROM Employees WHERE ID = @EMP_ID END
Tạo lớp JDBCCallableStatementExample và viết xử lý
package jdbc;
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
*
* @author giasutinhoc.vn
*/
public class JDBCCallableStatementExample {
// SQL Server JDBC connection string
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:sqlserver://localhost;databaseName=EMPDB;user=sa;password=sa";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
CallableStatement stmt = null;
try {
//Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL);
//Execute a query
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
String sql = "{call getEmpName (?, ?)}";
stmt = conn.prepareCall(sql);
//Bind IN parameter first, then bind OUT parameter
int empID = 100;
stmt.setInt(1, empID); // This would set ID as 100
// Because second parameter is OUT so register it
stmt.registerOutParameter(2, java.sql.Types.NVARCHAR);
//Use execute method to run stored procedure.
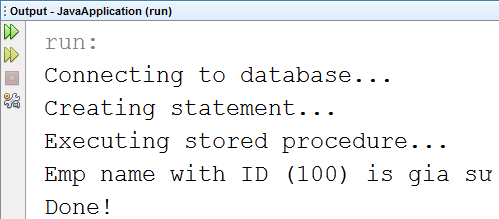
System.out.println("Executing stored procedure...");
stmt.execute();
//Retrieve employee name with getXXX method
String empName = stmt.getString(2);
System.out.println("Emp name with ID (" + empID + ") is " + empName);
stmt.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
//Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
} catch (SQLException se2) {
se2.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
}//end finally try
}//end try
System.out.println("Done!");
}
}
Khi chạy chương trình trên, chúng ta sẽ nhận được kết quả sau
JDBC Statement trong java – Các bước xử lý
Bước 1: Thiết lập kết nối đến máy chủ cơ sở dữ liệu
Bước 2: Tạo đối tượng thực thi câu lệnh SQL (Statement, PrepareStatement hoặc CallableStatement)
Bước 3: Viết câu lệnh SQL, thực thi câu lệnh SQL và xử lý kết quả (nếu có)
Bước 4: Đóng kết nối
JDBC Statement trong java – Tổng kết
- Thực thi câu lệnh SQL tĩnh với Statement
- Thực thi câu lệnh SQL có tham số với PreparedStatement
- Thực thi thủ tục với CallableStatement